Difference between revisions of "China"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Origin== | ==Origin== | ||
| − | late 16th century (as an adjective): from Persian chīnī ‘relating to China’, where it was originally made. | + | late [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/16th_century 16th century] (as an adjective): from Persian chīnī ‘relating to China’, where it was originally made. |
==Descriptions== | ==Descriptions== | ||
*1. A fine white or translucent vitrified ceramic material | *1. A fine white or translucent vitrified ceramic material | ||
Latest revision as of 15:06, 21 December 2020
Origin
late 16th century (as an adjective): from Persian chīnī ‘relating to China’, where it was originally made.
Descriptions
- 1. A fine white or translucent vitrified ceramic material
- 2. a plate made of china : a china cup. Also called porcelain.
- 3. household tableware or other objects made from china or a similar ceramic material: the breakfast china.
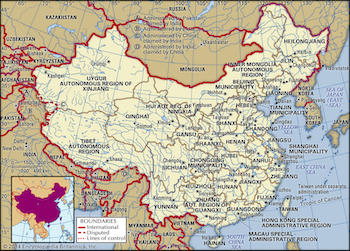
The country
A country in eastern Asia, the fourth largest and most populous in the world; population 1,376,000,000 (estimated 2015); capital, Beijing; language, Chinese (Mandarin is the official form). Official name People's Republic of China.
Chinese civilization stretches back until at least the 3rd millennium bc, the country being ruled by a series of dynasties until the Qing (or Manchu) dynasty was overthrown by Sun Yat-sen in 1911; China was proclaimed a republic the following year. After World War II, the Kuomintang government of Chiang Kai-shek was overthrown by the Communists under Mao Zedong, and the People's Republic of China was declared in 1949. Market-oriented reforms were introduced in the last quarter of the twentieth century.