Difference between revisions of "Chemical Elements"
m (Text replacement - "http://" to "https://") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:lighterstill.jpg]] | [[File:lighterstill.jpg]] | ||
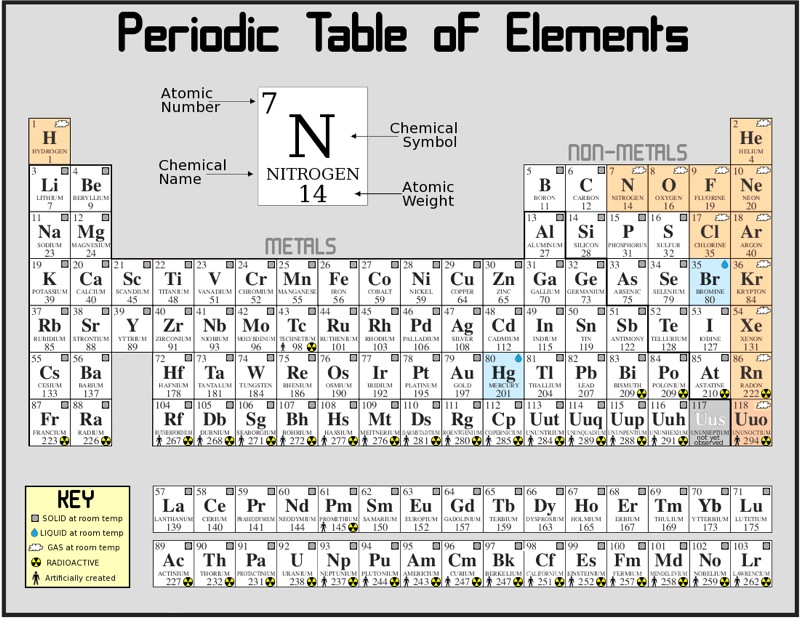
| − | The ''periodic table'' of the [[chemical]] ''elements'' (also periodic table of the elements or just periodic table) is a tabular display of the chemical elements. Although precursors to this table exist, its [[invention]] is generally credited to Russian chemist [ | + | The ''periodic table'' of the [[chemical]] ''elements'' (also periodic table of the elements or just periodic table) is a tabular display of the chemical elements. Although precursors to this table exist, its [[invention]] is generally credited to Russian chemist [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dmitri_Mendeleev Dmitri Mendeleev] in 1869, who intended the table to [[illustrate]] recurring ("periodic") [[trends]] in the properties of the elements. The layout of the table has been refined and extended over [[time]], as new elements have been [[discovered]], and new [[theoretical]] [[models]] have been [[developed]] to [[explain]] chemical [[behavior]]. |
The periodic table is now ubiquitous within the [[academic]] [[discipline]] of [[chemistry]], providing an extremely useful framework to [[classify]], systematize, and [[compare]] all of the many [[different]] [[forms]] of chemical [[behavior]]. The table has found wide [[application]] in [[chemistry]], [[physics]], [[biology]], and engineering, especially chemical engineering. The current standard table contains 118 elements as of March 2010 (elements 1–118). | The periodic table is now ubiquitous within the [[academic]] [[discipline]] of [[chemistry]], providing an extremely useful framework to [[classify]], systematize, and [[compare]] all of the many [[different]] [[forms]] of chemical [[behavior]]. The table has found wide [[application]] in [[chemistry]], [[physics]], [[biology]], and engineering, especially chemical engineering. The current standard table contains 118 elements as of March 2010 (elements 1–118). | ||
Latest revision as of 23:42, 12 December 2020
The periodic table of the chemical elements (also periodic table of the elements or just periodic table) is a tabular display of the chemical elements. Although precursors to this table exist, its invention is generally credited to Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, who intended the table to illustrate recurring ("periodic") trends in the properties of the elements. The layout of the table has been refined and extended over time, as new elements have been discovered, and new theoretical models have been developed to explain chemical behavior.
The periodic table is now ubiquitous within the academic discipline of chemistry, providing an extremely useful framework to classify, systematize, and compare all of the many different forms of chemical behavior. The table has found wide application in chemistry, physics, biology, and engineering, especially chemical engineering. The current standard table contains 118 elements as of March 2010 (elements 1–118).