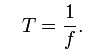Difference between revisions of "Frequency"
m (Text replacement - "http://" to "https://") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
'''Frequency''' is the [[number]] of occurrences of a repeating [[event]] per unit [[time]]. It is also referred to as [[temporal]] frequency. The period is the duration of one [[cycle]] in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. | '''Frequency''' is the [[number]] of occurrences of a repeating [[event]] per unit [[time]]. It is also referred to as [[temporal]] frequency. The period is the duration of one [[cycle]] in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. | ||
| − | <center>For lessons on the related [[topic]] of '''''[[Attunement]]''''', follow [ | + | <center>For lessons on the related [[topic]] of '''''[[Attunement]]''''', follow [https://nordan.daynal.org/wiki/index.php?title=Category:Attunement '''''this link'''''].</center> |
==Definitions and units== | ==Definitions and units== | ||
| − | For cyclical [[processes]], such as [ | + | For cyclical [[processes]], such as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotation rotation], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oscillation oscillations], or [[waves]], frequency is defined as a [[number]] of [[cycles]], or periods, per unit time. In [[physics]] and [[engineering]] [[disciplines]], such as [[optics]], [[acoustics]], and radio, frequency is usually denoted by a [[Latin]] letter f or by a Greek letter ν (nu). |
| − | In [ | + | In [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SI_derived_unit SI] units, the unit of frequency is hertz (Hz), named after the German physicist Heinrich Hertz. For example, 1 Hz means that an event repeats once per second. |
A [[traditional]] unit of [[measure]] used with rotating [[mechanical]] devices is the revolutions per minute, abbreviated rpm. 60 rpm equals one hertz.[1] | A [[traditional]] unit of [[measure]] used with rotating [[mechanical]] devices is the revolutions per minute, abbreviated rpm. 60 rpm equals one hertz.[1] | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| − | The SI unit for period is the second.[ | + | The SI unit for period is the second.[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frequency] |
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*'''''[[Amplitude]]''''' | *'''''[[Amplitude]]''''' | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
* Giancoli, D.C. (1988), Physics for Scientists and Engineers (2nd ed.), Prentice Hall, ISBN 013669201X | * Giancoli, D.C. (1988), Physics for Scientists and Engineers (2nd ed.), Prentice Hall, ISBN 013669201X | ||
| − | *Davies, A. (1997). Handbook of Condition Monitoring: Techniques and Methodology. New York: Springer. pp. 275. ISBN 9780412613203. | + | *Davies, A. (1997). Handbook of Condition Monitoring: Techniques and Methodology. New York: Springer. pp. 275. ISBN 9780412613203. https://books.google.com/books?id=j2mN2aIs2YIC&pg=RA1-PA275. |
| − | *Bakshi, K.A.; A.V. Bakshi, U.A. Bakshi (2008). Electronic Measurement Systems. US: Technical Publications. pp. 4-14. ISBN 9788184312065. | + | *Bakshi, K.A.; A.V. Bakshi, U.A. Bakshi (2008). Electronic Measurement Systems. US: Technical Publications. pp. 4-14. ISBN 9788184312065. https://books.google.com/books?id=jvnI3Dar3b4C&pg=PT183. |
| − | *Elert, Glenn; Timothy Condon (2003). "Frequency Range of Dog Hearing" (in English). The Physics Factbook. | + | *Elert, Glenn; Timothy Condon (2003). "Frequency Range of Dog Hearing" (in English). The Physics Factbook. https://hypertextbook.com/facts/2003/TimCondon.shtml. Retrieved 2008-10-22. |
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | * [ | + | * [https://inms-ienm.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/research/optical_frequency_projects_e.html#femtosecond National Research Council of Canada: ''Femtosecond comb; The measurement of optical frequencies''] |
| − | * [ | + | * [https://www.sengpielaudio.com/calculator-wavelength.htm Conversion: frequency to wavelength and back] |
| − | * [ | + | * [https://www.sengpielaudio.com/calculator-period.htm Conversion: period, cycle duration, periodic time to frequency] |
| − | * [ | + | * [https://www.sengpielaudio.com/calculator-notenames.htm Keyboard frequencies = naming of notes - The English and American system versus the German system] |
| − | * [ | + | * [https://www.acoustics.salford.ac.uk/schools/index1.htm Teaching resource for 14-16yrs on sound including frequency] |
| − | * [ | + | * [https://www.ikalogic.com/freq_meter.php A simple tutorial on how to build a frequency meter] |
| − | * [ | + | * [https://www.diracdelta.co.uk/science/source/f/r/frequency/source.html Frequency - diracdelta.co.uk] - [[javascript]] calculation. |
[[Category: Physics]] | [[Category: Physics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:03, 13 December 2020
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency. The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency.
Definitions and units
For cyclical processes, such as rotation, oscillations, or waves, frequency is defined as a number of cycles, or periods, per unit time. In physics and engineering disciplines, such as optics, acoustics, and radio, frequency is usually denoted by a Latin letter f or by a Greek letter ν (nu).
In SI units, the unit of frequency is hertz (Hz), named after the German physicist Heinrich Hertz. For example, 1 Hz means that an event repeats once per second.
A traditional unit of measure used with rotating mechanical devices is the revolutions per minute, abbreviated rpm. 60 rpm equals one hertz.[1]
The period is usually denoted as T, and is the reciprocal of the frequency f:
The SI unit for period is the second.[1]
See also
References
- Giancoli, D.C. (1988), Physics for Scientists and Engineers (2nd ed.), Prentice Hall, ISBN 013669201X
- Davies, A. (1997). Handbook of Condition Monitoring: Techniques and Methodology. New York: Springer. pp. 275. ISBN 9780412613203. https://books.google.com/books?id=j2mN2aIs2YIC&pg=RA1-PA275.
- Bakshi, K.A.; A.V. Bakshi, U.A. Bakshi (2008). Electronic Measurement Systems. US: Technical Publications. pp. 4-14. ISBN 9788184312065. https://books.google.com/books?id=jvnI3Dar3b4C&pg=PT183.
- Elert, Glenn; Timothy Condon (2003). "Frequency Range of Dog Hearing" (in English). The Physics Factbook. https://hypertextbook.com/facts/2003/TimCondon.shtml. Retrieved 2008-10-22.
External links
- National Research Council of Canada: Femtosecond comb; The measurement of optical frequencies
- Conversion: frequency to wavelength and back
- Conversion: period, cycle duration, periodic time to frequency
- Keyboard frequencies = naming of notes - The English and American system versus the German system
- Teaching resource for 14-16yrs on sound including frequency
- A simple tutorial on how to build a frequency meter
- Frequency - diracdelta.co.uk - javascript calculation.