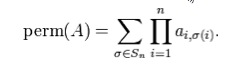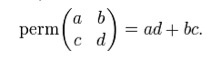Difference between revisions of "Permanent"
(Created page with 'File:lighterstill.jpgright|frame ==Etymology== [http://nordan.daynal.org/wiki/index.php?title=English#ca._1100-1500_.09THE_MIDDLE_ENGLISH_PERIOD Middle...') |
m (Text replacement - "http://" to "https://") |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
| − | [ | + | [https://nordan.daynal.org/wiki/index.php?title=English#ca._1100-1500_.09THE_MIDDLE_ENGLISH_PERIOD Middle English], from Anglo-French parmanant, from [[Latin]] permanent-, permanens, present participle of permanēre to [[endure]], from per- throughout + manēre to remain |
| − | *Date: [ | + | *Date: [https://www.wikipedia.org/wiki/15th_Century 15th century] |
==Definition== | ==Definition== | ||
*continuing or [[enduring]] without [[fundamental]] or marked [[change]] : [[stable]] | *continuing or [[enduring]] without [[fundamental]] or marked [[change]] : [[stable]] | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| − | In [ | + | In [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_algebra linear algebra], the '''permanent''' of a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Square_matrix square matrix] is a [[function]] of the matrix similar to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Determinant determinant]. The permanent, as well as the determinant, is a polynomial in the entries of the matrix. Both permanent and determinant are special cases of a more general function of a matrix called the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immanant immanant]. |
The permanent of an n-by-n matrix A = (ai,j) is defined as | The permanent of an n-by-n matrix A = (ai,j) is defined as | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
:[[File:Perm_2.jpg]] | :[[File:Perm_2.jpg]] | ||
| − | The definition of the permanent of A [[differs]] from that of the determinant of A in that the signatures of the [ | + | The definition of the permanent of A [[differs]] from that of the determinant of A in that the signatures of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Permutations permutations] are not taken into account. If one [[views]] the permanent as a map that takes n [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_vector vectors] as [[arguments]], then it is a multilinear map and it is [[symmetric]] ([[meaning]] that any order of the vectors results in the same permanent). A [[formula]] similar to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expansion_by_minors Laplace's] for the [[development]] of a determinant along a row or column is also valid for the permanent; all [[signs]] have to be ignored for the permanent. |
| − | The permanent is [[believed]] to be more [[difficult]] to compute than the determinant. While the determinant can be computed in polynomial time by [ | + | The permanent is [[believed]] to be more [[difficult]] to compute than the determinant. While the determinant can be computed in polynomial time by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaussian_elimination Gaussian elimination], Gaussian elimination cannot be used to compute the permanent. Moreover, computing the permanent of a 0-1 [[matrix]] (matrix whose entries are 0 or 1) is #P-complete. Thus, if the permanent can be computed in polynomial time by any [[method]], then FP = #P which is an even stronger [[statement]] than P = NP. When the entries of A are nonnegative, however, the permanent can be computed approximately in [[probabilistic]] polynomial time, up to an error of εM, where M is the [[value]] of the permanent and ε > 0 is [[arbitrary]]. |
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | * Permanent at [ | + | * Permanent at [https://planetmath.org/encyclopedia/Permanent.html PlanetMath] |
[[Category: General Reference]] | [[Category: General Reference]] | ||
[[Category: Mathematics]] | [[Category: Mathematics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:36, 13 December 2020
Etymology
Middle English, from Anglo-French parmanant, from Latin permanent-, permanens, present participle of permanēre to endure, from per- throughout + manēre to remain
- Date: 15th century
Definition
- continuing or enduring without fundamental or marked change : stable
Description
In linear algebra, the permanent of a square matrix is a function of the matrix similar to the determinant. The permanent, as well as the determinant, is a polynomial in the entries of the matrix. Both permanent and determinant are special cases of a more general function of a matrix called the immanant.
The permanent of an n-by-n matrix A = (ai,j) is defined as
The sum here extends over all elements σ of the symmetric group Sn, i.e. over all permutations of the numbers 1, 2, ..., n.
For example,
The definition of the permanent of A differs from that of the determinant of A in that the signatures of the permutations are not taken into account. If one views the permanent as a map that takes n vectors as arguments, then it is a multilinear map and it is symmetric (meaning that any order of the vectors results in the same permanent). A formula similar to Laplace's for the development of a determinant along a row or column is also valid for the permanent; all signs have to be ignored for the permanent.
The permanent is believed to be more difficult to compute than the determinant. While the determinant can be computed in polynomial time by Gaussian elimination, Gaussian elimination cannot be used to compute the permanent. Moreover, computing the permanent of a 0-1 matrix (matrix whose entries are 0 or 1) is #P-complete. Thus, if the permanent can be computed in polynomial time by any method, then FP = #P which is an even stronger statement than P = NP. When the entries of A are nonnegative, however, the permanent can be computed approximately in probabilistic polynomial time, up to an error of εM, where M is the value of the permanent and ε > 0 is arbitrary.
External links
- Permanent at PlanetMath