Difference between revisions of "Siphon"
(Created page with 'File:lighterstill.jpgright|frame ==Origin== French ''siphon'', from Latin ''siphon''-, ''sipho'' tube, pipe, siphon, from Greek ''siphōn'' *[http://en...') |
m (Text replacement - "http://" to "https://") |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Origin== | ==Origin== | ||
French ''siphon'', from Latin ''siphon''-, ''sipho'' tube, pipe, siphon, from Greek ''siphōn'' | French ''siphon'', from Latin ''siphon''-, ''sipho'' tube, pipe, siphon, from Greek ''siphōn'' | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/17th_century 1659] |
==Definitions== | ==Definitions== | ||
*1a : a tube bent to form two legs of unequal length by which a [[liquid]] can be transferred to a lower level over an [[intermediate]] elevation by the [[pressure]] of the [[atmosphere]] in forcing the liquid up the shorter branch of the tube immersed in it while the excess of [[weight]] of the [[liquid]] in the longer branch when once filled causes a [[continuous]] [[flow]] | *1a : a tube bent to form two legs of unequal length by which a [[liquid]] can be transferred to a lower level over an [[intermediate]] elevation by the [[pressure]] of the [[atmosphere]] in forcing the liquid up the shorter branch of the tube immersed in it while the excess of [[weight]] of the [[liquid]] in the longer branch when once filled causes a [[continuous]] [[flow]] | ||
:b usually syphon : a bottle for holding aerated water that is driven out through a bent tube in its neck by the [[pressure]] of the [[gas]] when a valve in the tube is opened | :b usually syphon : a bottle for holding aerated water that is driven out through a bent tube in its neck by the [[pressure]] of the [[gas]] when a valve in the tube is opened | ||
| − | *2: any of various tubular organs in [[animals]] and especially [ | + | *2: any of various tubular organs in [[animals]] and especially [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mollusk mollusks] or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arthropods arthropods] that are used for drawing in or ejecting [[fluid]]s. |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
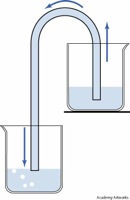
| − | The word '''siphon''' (Greek: Σίφων, also spelled ''syphon'') is sometimes used to refer to a wide [[variety]] of devices that involve the [[flow]] of liquids through tubes. But in the [[English]] language today, the [[word]] siphon usually refers to a tube in an inverted U shape which causes a [[liquid]] to flow uphill, above the [[surface]] of the [[reservoir]], without pumps, powered by the fall of the liquid as it flows down the tube under the pull of [[gravity]], and is discharged at a level lower than the [[surface]] of the reservoir. In [[practical]] siphons, [[atmospheric]] [[pressure]] pushes the liquid up the tube into the region of reduced pressure at the top of the tube. The reduced pressure is caused by [[liquid]] falling on the exit side. In the [[laboratory]], some siphons have been [[demonstrated]] to work in a vacuum, indicating the [ | + | The word '''siphon''' (Greek: Σίφων, also spelled ''syphon'') is sometimes used to refer to a wide [[variety]] of devices that involve the [[flow]] of liquids through tubes. But in the [[English]] language today, the [[word]] siphon usually refers to a tube in an inverted U shape which causes a [[liquid]] to flow uphill, above the [[surface]] of the [[reservoir]], without pumps, powered by the fall of the liquid as it flows down the tube under the pull of [[gravity]], and is discharged at a level lower than the [[surface]] of the reservoir. In [[practical]] siphons, [[atmospheric]] [[pressure]] pushes the liquid up the tube into the region of reduced pressure at the top of the tube. The reduced pressure is caused by [[liquid]] falling on the exit side. In the [[laboratory]], some siphons have been [[demonstrated]] to work in a vacuum, indicating the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tensile_strength tensile strength] of the liquid is contributing to the operation of siphons at very low [[pressures]]. |
[[Category: General Reference]] | [[Category: General Reference]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:50, 13 December 2020
Origin
French siphon, from Latin siphon-, sipho tube, pipe, siphon, from Greek siphōn
Definitions
- 1a : a tube bent to form two legs of unequal length by which a liquid can be transferred to a lower level over an intermediate elevation by the pressure of the atmosphere in forcing the liquid up the shorter branch of the tube immersed in it while the excess of weight of the liquid in the longer branch when once filled causes a continuous flow
- b usually syphon : a bottle for holding aerated water that is driven out through a bent tube in its neck by the pressure of the gas when a valve in the tube is opened
- 2: any of various tubular organs in animals and especially mollusks or arthropods that are used for drawing in or ejecting fluids.
Description
The word siphon (Greek: Σίφων, also spelled syphon) is sometimes used to refer to a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. But in the English language today, the word siphon usually refers to a tube in an inverted U shape which causes a liquid to flow uphill, above the surface of the reservoir, without pumps, powered by the fall of the liquid as it flows down the tube under the pull of gravity, and is discharged at a level lower than the surface of the reservoir. In practical siphons, atmospheric pressure pushes the liquid up the tube into the region of reduced pressure at the top of the tube. The reduced pressure is caused by liquid falling on the exit side. In the laboratory, some siphons have been demonstrated to work in a vacuum, indicating the tensile strength of the liquid is contributing to the operation of siphons at very low pressures.