Difference between revisions of "Dropsy"
m (Text replacement - "http://nordan.daynal.org" to "https://nordan.daynal.org") |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Origin== | ==Origin== | ||
| − | [ | + | [https://nordan.daynal.org/wiki/index.php?title=English#ca._1100-1500_.09THE_MIDDLE_ENGLISH_PERIOD Middle English] dropesie, short for ydropesie, from Anglo-French, from [[Latin]] hydropisis, modification of [[Greek]] hydrōps, from hydōr water — more at [[water]] |
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/13th_century 13th Century] | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/13th_century 13th Century] | ||
==Definitions== | ==Definitions== | ||
Revision as of 22:10, 12 December 2020
Origin
Middle English dropesie, short for ydropesie, from Anglo-French, from Latin hydropisis, modification of Greek hydrōps, from hydōr water — more at water
Definitions
- 1: Edema
- a.: an abnormal infiltration and excess accumulation of serous fluid in connective tissue or in a serous cavity —called also dropsy
- b : watery swelling of plant organs or parts
- c : any of various plant diseases characterized by such swellings
Description
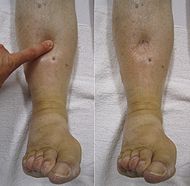
Edema (American English) or oedema (British English; both words from the Greek οἴδημα, oídēma "swelling"), formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body. Generally, the amount of interstitial fluid is determined by the balance of fluid homeostasis, and increased secretion of fluid into the interstitium or impaired removal of this fluid may cause edema.
Classification
Cutaneous edema is referred to as "pitting" when, after pressure is applied to a small area, the indentation persists for some time after the release of the pressure. Peripherial pitting edema, is the more common type, results in water retention. It can be caused by systemic diseases, pregnancy in some women, either directly or as a result of heart failure, or local conditions such as varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, insect bites, and dermatitis.
Non-pitting edema is observed when the indentation does not persist. It is associated with such conditions as lymphedema, Lipoedema and myxedema.[1]