Difference between revisions of "Light year"
m (Text replacement - "http://" to "https://") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
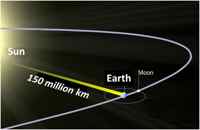
[[File:lighterstill.jpg]][[File:Sun_to_Earth.jpg|right|frame|<center>[[Light]] takes about 8 minutes,19 seconds to reach [[Earth]].</center>]] | [[File:lighterstill.jpg]][[File:Sun_to_Earth.jpg|right|frame|<center>[[Light]] takes about 8 minutes,19 seconds to reach [[Earth]].</center>]] | ||
| − | A '''light-year''' or [[light]] year (symbol: ly) is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion (i.e. 1013) kilometres. As defined by the [ | + | A '''light-year''' or [[light]] year (symbol: ly) is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion (i.e. 1013) kilometres. As defined by the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Astronomical_Union International Astronomical Union] (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a [[vacuum]] in one Julian year. |
| − | The [[light]]-year is often used to [[measure]] distances to [[stars]] and other [[distances]] on a [[Galaxy|galactic]] scale, especially in non-specialist and [ | + | The [[light]]-year is often used to [[measure]] distances to [[stars]] and other [[distances]] on a [[Galaxy|galactic]] scale, especially in non-specialist and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Popular_science popular science] publications. The preferred unit in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Astrometry astrometry] is the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parsec parsec], because it can be more easily derived from, and compared with, [[observation]]al [[data]]. The parsec is defined as the distance at which an object will appear to move one [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcsecond arcsecond] of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parallax parallax] when the observer moves one [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Astronomical_unit astronomical unit] perpendicular to the line of sight to the [[observer]], and is [[equal]] to approximately 3.26 light-years. |
The related unit of the light-month, roughly one-twelfth of a light-year, is also used occasionally for approximate measures. | The related unit of the light-month, roughly one-twelfth of a light-year, is also used occasionally for approximate measures. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
* about 0.306601 parsecs | * about 0.306601 parsecs | ||
| − | The figures above are based on a [ | + | The figures above are based on a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Julian_year_(astronomy) Julian year] (not Gregorian year) of exactly 365.25 days (each of exactly 86,400 SI seconds, totalling 31,557,600 seconds)[4] and a defined speed of light of 299,792,458 m/s, both included in the IAU (1976) [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Astronomical_constant System of Astronomical Constants], used since 1984. The DE405 value of the astronomical unit, 149,597,870,691 m, is used for the light-year in astronomical units and parsecs.[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light_year] |
[[Category: Astronomy]] | [[Category: Astronomy]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:36, 13 December 2020
A light-year or light year (symbol: ly) is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion (i.e. 1013) kilometres. As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year.
The light-year is often used to measure distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist and popular science publications. The preferred unit in astrometry is the parsec, because it can be more easily derived from, and compared with, observational data. The parsec is defined as the distance at which an object will appear to move one arcsecond of parallax when the observer moves one astronomical unit perpendicular to the line of sight to the observer, and is equal to approximately 3.26 light-years.
The related unit of the light-month, roughly one-twelfth of a light-year, is also used occasionally for approximate measures.
Numerical value
A light-year is equal to:
- exactly 9,460,730,472,580.8 km (about 10 Pm)
- about 5,878,630,000,000 miles (about 6 trillion miles)
- about 63,241.1 astronomical units
- about 0.306601 parsecs
The figures above are based on a Julian year (not Gregorian year) of exactly 365.25 days (each of exactly 86,400 SI seconds, totalling 31,557,600 seconds)[4] and a defined speed of light of 299,792,458 m/s, both included in the IAU (1976) System of Astronomical Constants, used since 1984. The DE405 value of the astronomical unit, 149,597,870,691 m, is used for the light-year in astronomical units and parsecs.[1]