Difference between revisions of "Modern"
m (Text replacement - "http://" to "https://") |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
Late Latin modernus, from Latin modo just now, from modus [[measure]] | Late Latin modernus, from Latin modo just now, from modus [[measure]] | ||
| − | *Date: [ | + | *Date: [https://www.wikpedia.org/wiki/16th_Century 1585] |
==Definitions== | ==Definitions== | ||
*1 a : of, relating to, or characteristic of the present or the [[immediate]] [[past]] : contemporary | *1 a : of, relating to, or characteristic of the present or the [[immediate]] [[past]] : contemporary | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
*3 capitalized : of, relating to, or having the characteristics of the present or most recent period of [[development]] of a [[language]] | *3 capitalized : of, relating to, or having the characteristics of the present or most recent period of [[development]] of a [[language]] | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| − | '''Modern''' [[history]], or the modern era, describes the historical [[timeline]] after the [ | + | '''Modern''' [[history]], or the modern era, describes the historical [[timeline]] after the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_ages Middle Ages]. Modern history can be further broken down into the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Early_modern_period early modern period] and the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Late_modern_period late modern period]. Contemporary [[history]] describes the span of historic [[events]] that are immediately relevant to the [[present]] [[time]]. |
| − | The beginning of the modern era started approximately in the [ | + | The beginning of the modern era started approximately in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/16th_Century 1500]s. Many major [[events]] caused the Western world to change around the turn of the 16th century, starting with the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fall_of_Constantinople Fall of Constantinople] in 1453, the fall of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muslim_Spain Muslim Spain] and the [[discovery]] of the [[America]]s in 1492, and Martin Luther's [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protestant_Reformation Protestant Reformation] in 1517. In England the modern period is often dated to the start of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tudor_period Tudor period] with the victory of Henry VII over Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth in 1485. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Early_modern_Europe Early modern European history] is usually seen to span from the turn of the 15th century, through the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Age_of_Reason Age of Reason] and [[Age of Enlightenment]] in the 17th and 18th centuries, until the beginning of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industrial_Revolution Industrial Revolution] in the late 18th century.[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modern] |
[[Category: History]] | [[Category: History]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:24, 13 December 2020
Etymology
Late Latin modernus, from Latin modo just now, from modus measure
- Date: 1585
Definitions
- b : of, relating to, or characteristic of a period extending from a relevant remote past to the present time
- 2 : involving recent techniques, methods, or ideas : up-to-date
- 3 capitalized : of, relating to, or having the characteristics of the present or most recent period of development of a language
Description
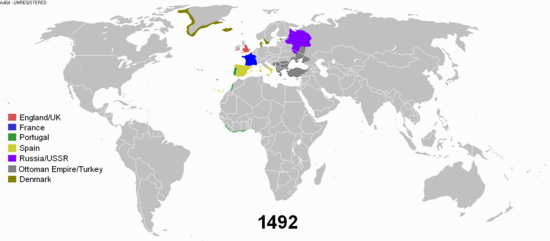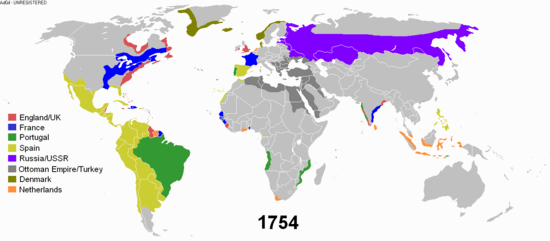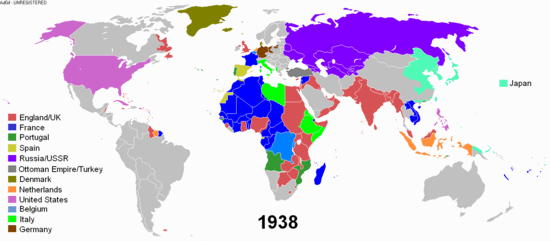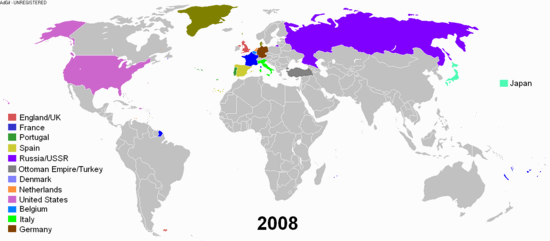
Modern history, or the modern era, describes the historical timeline after the Middle Ages. Modern history can be further broken down into the early modern period and the late modern period. Contemporary history describes the span of historic events that are immediately relevant to the present time.
The beginning of the modern era started approximately in the 1500s. Many major events caused the Western world to change around the turn of the 16th century, starting with the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, the fall of Muslim Spain and the discovery of the Americas in 1492, and Martin Luther's Protestant Reformation in 1517. In England the modern period is often dated to the start of the Tudor period with the victory of Henry VII over Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth in 1485. Early modern European history is usually seen to span from the turn of the 15th century, through the Age of Reason and Age of Enlightenment in the 17th and 18th centuries, until the beginning of the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century.[1]