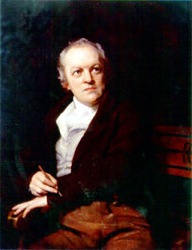|
|
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | [[Image:lighterstill.jpg]] | | [[Image:lighterstill.jpg]] |
| − | [[Image:WilliamBlakebyThomasPhillips.jpg|right|frame|Portrait by Thomas Phillips]] | + | [[Image:WilliamBlakebyThomasPhillips.jpg|right|frame|<center>Portrait of Wm. Blake by Thomas Phillips</center>]] |
| | | | |
| − | '''William Blake''' ([[November 28]], [[1757]] – [[August 12]], [[1827]]) was an [[England|English]] [[English poetry|poet]], [[Painting|painter]], and [[printmaker]]. Largely unrecognized during his lifetime, Blake's work is now considered seminal in the history of both poetry and the visual arts. | + | '''William Blake''' (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English painter, [[poet]] and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his lifetime, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the [[history]] of the [[poetry]] and visual arts of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Romanticism Romantic Age]. His [[prophetic]] poetry has been said to form "what is in [[proportion]] to its merits the least read body of poetry in the English language". His visual artistry led one contemporary art critic to proclaim him "far and away the greatest artist Britain has ever produced". In 2002, Blake was placed at number 38 in the BBC's poll of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/100_Greatest_Britons 100 Greatest Britons]. Although he lived in London his entire life (except for three years spent in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Felpham Felpham]), he produced a diverse and [[symbolically]] rich oeuvre, which [[embraced]] the [[imagination]] as "the body of God" or "human existence itself". |
| | | | |
| − | Blake's prophetic poetry has been said to form "what is in proportion to its merits the least read body of poetry in the [[English language|(English) language]]".<ref>Frye, Northrop and Denham, Robert D. ''Collected Works of Northrop Frye''. 2006, page 11-2.</ref> His visual artistry has led one modern critic to proclaim him "far and away the greatest artist Britain has ever produced".<ref>{{cite web | author=Jones, Jonathan| year= April 2005| title= Blake's heaven |publisher=[[The Guardian]] | url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/arts/critic/feature/0,1169,1469584,00.html |date=[[2005-04-25]]}}</ref> Although he only once travelled any further than a day's walk outside London over the course of his life,<ref>Thomas, Edward. ''[http://books.google.com/books?id=bilDAAAAIAAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=A+Literary+Pilgrim+in+England A Literary Pilgrim in England]''. 1917, page 3.</ref> his creative vision engendered a diverse and symbolically rich corpus, which embraced '[[imagination]]' as "the body of God",<ref>[[William Butler Yeats|Yeats, W. B.]] ''The Collected Works of W. B. Yeats''. 2007, page 85.</ref> or "Human existence itself".<ref>Wilson, Mona. ''The Life of William Blake''. The Nonesuch Press, 1927. p.167.</ref> | + | Considered mad by contemporaries for his [[idiosyncratic]] views, Blake is held in high regard by later critics for his expressiveness and [[creativity]], and for the [[philosophical]] and [[mystical]] undercurrents within his work. His paintings and poetry have been characterised as part of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Romantic_movement Romantic movement] and "Pre-Romantic", for its large appearance in the 18th century. Reverent of the Bible but hostile to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Church_of_England Church of England] (indeed, to all forms of organised religion), Blake was influenced by the ideals and ambitions of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/French_Revolution French] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_Revolution American Revolutions]. Though later he rejected many of these political [[beliefs]], he maintained an amiable [[relationship]] with the political activist [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thomas_Paine Thomas Paine]; he was also influenced by thinkers such as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emanuel_Swedenborg Emanuel Swedenborg]. Despite these known influences, the singularity of Blake's work makes him difficult to classify. The 19th-century scholar [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Rossetti William Rossetti] characterised him as a "glorious luminary", and "a man not forestalled by predecessors, nor to be classed with contemporaries, nor to be replaced by known or readily surmisable successors". |
| | | | |
| − | Once considered mad for his idiosyncratic views, Blake is highly regarded today for his expressiveness and creativity, as well as the philosophical and mystical undercurrents that reside within his work. His work has been characterized as part of the [[Romantic movement]], or even "Pre-Romantic",<ref>''The New York Times Guide to Essential Knowledge''. 2004, page 351.</ref> for its largely having appeared in the 18th century. Reverent of the [[Bible]] but hostile to the [[Church of England|established Church]], Blake was influenced by the ideals and ambitions of the [[French revolution|French]] and [[American revolution]]s,<ref>Blake, William. ''Blake's "America, a Prophecy" ; And, "Europe, a Prophecy"''. 1984, page 2.</ref> as well as by such thinkers as [[Jacob Boehme]] and [[Emanuel Swedenborg]].<ref>{{cite web | author=Kazin, Alfred | year=1997 | title= An Introduction to William Blake |url=http://www.multimedialibrary.com/Articles/kazin/alfredblake.asp |accessdate=2006-09-23}}</ref>
| + | Because Blake's later poetry contains a private [[mythology]] with complex [[symbolism]], his late work has been less published than his earlier more accessible work. The Vintage anthology of Blake edited by Patti Smith focuses heavily on the earlier work, as do many critical studies such as William Blake by D. G. Gillham. |
| | | | |
| − | Despite these known influences, the originality and singularity of Blake's work make it difficult to classify. One 19th century scholar characterised Blake as a "glorious luminary,"<ref>Blake, William and Rossetti, William Michael. ''[http://books.google.com/books?id=fGYLAAAAIAAJ&pg=PP11&dq=%22The+Poetical+Works+of+William+Blake:+Lyrical+and+Miscellaneous%22&lr=&as_brr=3 The Poetical Works of William Blake: Lyrical and Miscellaneous]''. 1890, page xi.</ref> "a man not forestalled by predecessors, nor to be classed with contemporaries, nor to be replaced by known or readily surmisable successors."<ref>Blake, William and Rossetti, William Michael. ''[http://books.google.com/books?id=fGYLAAAAIAAJ&pg=PP11&dq=%22The+Poetical+Works+of+William+Blake:+Lyrical+and+Miscellaneous%22&lr=&as_brr=3 The Poetical Works of William Blake: Lyrical and Miscellaneous]''. 1890, page xiii.</ref>
| + | The earlier work is primarily [[rebellious]] in character and can be seen as a protest against [[dogmatic]] religion especially notable in ''The Marriage of Heaven and Hell'', in which the figure represented by the "Devil" is virtually a hero rebelling against an imposter authoritarian deity. In later works, such as ''Milton'' and ''Jerusalem'', Blake carves a distinctive [[vision]] of a [[humanity]] redeemed by self-sacrifice and [[forgiveness]], while retaining his earlier negative [[attitude]] towards what he felt was the rigid and morbid authoritarianism of [[traditional]] [[religion]]. Not all readers of Blake agree upon how much continuity exists between Blake's earlier and later works. |
| | | | |
| − | ==Early life==
| + | [[Psychoanalyst]] June Singer has written that Blake's late work displayed a [[development]] of the [[ideas]] first introduced in his earlier works, namely, the humanitarian goal of achieving personal [[wholeness]] of [[body]] and [[spirit]]. The final section of the expanded edition of her Blake study The Unholy Bible suggests the later works are the "Bible of Hell" promised in The Marriage of Heaven and Hell. Regarding Blake's final poem "Jerusalem", she writes: "[T]he promise of the [[divine]] in man, made in ''The Marriage of Heaven and Hell'', is at last fulfilled."[62] |
| − | William Blake was born in 28A Broad Street, [[Golden Square]], [[London]], [[England]] on 28 November 1757, to a middle-class family. He was the third of 7 children,<ref>[http://www.poets.org/poet.php/prmPID/116 poets.org/William Blake, retrieved online June 13, 2008]</ref><ref name=bent>Bentley, Gerald Eades and Bentley Jr., G. ''William Blake: The Critical Heritage''. 1995, page 34-5.</ref> two of whom died in infancy. Blake's father, James, was a [[hosier]].<ref name=bent /> He never attended school, being educated at home by his mother.<Ref name="Raine">{{Cite book |author=Raine, Kathleen |title=World of Art: William Blake |publisher=Thames & Hudson |year=1970 |id=ISBN 0-500-20107-2}}</ref> The Blakes were [[Dissenter]]s, and are believed to have belonged to the [[Moravian Church]]. The [[Bible]] was an early and profound influence on Blake, and would remain a source of inspiration throughout his life.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Blake began [[engraving]] copies of drawings of [[ancient Greece|Greek]] antiquities purchased for him by his father, a practice that was then preferred to actual [[drawing]]. Within these drawings Blake found his first exposure to classical forms, through the work of [[Raphael]], [[Michelangelo]], [[Marten Jacobszoon Heemskerk van Veen|Marten Heemskerk]] and [[Albrecht Dürer]]. His parents knew enough of his headstrong temperament that he was not sent to school but was instead enrolled in drawing classes. He read avidly on subjects of his own choosing. During this period, Blake was also making explorations into poetry; his early work displays knowledge of [[Ben Jonson]] and [[Edmund Spenser]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Apprenticeship to Basire===
| |
| − | | |
| − | On [[4 August]] [[1772]], Blake became apprenticed to [[engraver]] [[James Basire]] of [[Great Queen Street]], for the term of seven years.<ref name=bent /> At the end of this period, at the age of 21, he was to become a professional engraver.
| |
| − | | |
| − | There is no record of any serious disagreement or conflict between the two during the period of Blake's apprenticeship. However, [[Peter Ackroyd]]'s biography notes that Blake was later to add Basire's name to a list of artistic adversaries—and then cross it out.<ref>43, ''Blake'', Peter Ackroyd, Sinclair-Stevenson, 1995</ref> This aside, Basire's style of engraving was of a kind held to be old-fashioned at the time,<ref>Blake, William. ''The Poems of William Blake''. 1893, page xix.</ref> and Blake's instruction in this outmoded form may have been detrimental to his acquiring of work or recognition in later life.
| |
| − | | |
| − | After two years Basire sent him to copy images from the [[Gothic architecture|Gothic]] churches in London (it is possible that this task was set in order to break up a quarrel between Blake and James Parker, his fellow apprentice), and his experiences in [[Westminster Abbey]] contributed to the formation of his artistic style and ideas; the Abbey of his day was decorated with suits of armour, painted funeral effigies and varicoloured waxworks. Ackroyd notes that "the most immediate [impression] would have been of faded brightness and colour".<ref>44, ''Blake'', Ackroyd</ref> In the long afternoons Blake spent sketching in the Abbey, he was occasionally interrupted by the boys of [[Westminster School]], one of whom "tormented" Blake so much one afternoon that he knocked the boy off a scaffold to the ground, "upon which he fell with terrific Violence".<ref>Blake, William and Tatham, Frederick. ''[http://books.google.com/books?id=cSxDAAAAIAAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=The+Letters+of+William+Blake:+Together+with+a+Life&lr=&as_brr=3 The Letters of William Blake: Together with a Life]''. 1906, page 7.</ref> Blake beheld more visions in the Abbey, of a great procession of monks and priests, while he heard "the chant of [[plain-song]] and [[chorale]]".
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===The Royal Academy===
| |
| − | In 1778, Blake became a student at the [[Royal Academy]] in Old Somerset House, near the [[Strand, London|Strand]]. While the terms of his study required no payment, he was expected to supply his own materials throughout the six-year period. There, he rebelled against what he regarded as the unfinished style of fashionable painters such as [[Peter Paul Rubens|Rubens]], championed by the school's first president, [[Joshua Reynolds]]. Over time, Blake came to detest Reynolds' attitude toward art, especially his pursuit of "general truth" and "general beauty". Reynolds wrote in his ''Discourses'' that the "disposition to abstractions, to generalizing and classification, is the great glory of the human mind"; Blake responded, in marginalia to his personal copy, that "To Generalize is to be an Idiot; To Particularize is the Alone Distinction of Merit".<ref>{{cite book |author=Erdman, David V |title=The Complete Poetry and Prose of William Blake |edition=2nd edition |pages=p641 |id=ISBN 0-385-15213-2}}</ref> Blake also disliked Reynolds' apparent humility, which he held to be a form of hypocrisy. Against Reynolds' fashionable [[oil painting]], Blake preferred the [[Classicism|Classical]] precision of his early influences, [[Michelangelo]] and [[Raffaello Santi|Raphael]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Gordon Riots===
| |
| − | Blake's first biographer [[Alexander Gilchrist]] records that in June 1780, Blake was walking towards Basire's shop in Great Queen Street when he was swept up by a rampaging mob that stormed [[Newgate Prison]] in London.<ref> Gilchrist, A, ''The Life of William Blake'', London, 1842, p. 30</ref> They attacked the prison gates with shovels and pickaxes, set the building ablaze, and released the prisoners inside. Blake was reportedly in the front rank of the mob during this attack. These riots, in response to a parliamentary bill revoking sanctions against [[Roman Catholicism]], later came to be known as the [[Gordon Riots]]; they provoked a flurry of legislation from the government of [[George III of the United Kingdom|George III]], as well as the creation of the first [[police]] force.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Despite Gilchrist's insistence that Blake was "forced" to accompany the crowd, some biographers have argued that he accompanied it impulsively, or supported it as a revolutionary act.<ref> Erdman, David, ''Prophet Against Empire'', p. 9</ref> In contrast, Jerome McGann argues that the riots were reactionary, and that events would have provoked "disgust" in Blake.<ref>McGann, J. "Did Blake Betray the French Revolution", ''Presenting Poetry: Composition, Publication, Reception'', Cambridge University Press, 1995, p.128</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Marriage and early career===
| |
| − | | |
| − | In 1782, Blake met [[John Flaxman]], who was to become his patron, and Catherine Boucher, who was to become his wife. At the time, Blake was recovering from a relationship that had culminated in a refusal of his marriage proposal. Telling Catherine and her parents the story, she expressed her sympathy, whereupon Blake asked her, "Do you pity me?" To Catherine's affirmative response he responded, "Then I love you." Blake married Catherine – who was five years his junior – on [[18 August]] [[1782]] in [[St. Mary's Church, Battersea]]. Illiterate, Catherine signed her wedding contract with an 'X'. Later, in addition to teaching Catherine to read and write, Blake trained her as an engraver; throughout his life she would prove an invaluable aid to him, helping to print his [[Illuminated manuscript|illuminated works]] and maintaining his spirits throughout numerous misfortunes.
| |
| − | | |
| − | At this time George Cumberland, one of the founders of the [[National Gallery, London|National Gallery]], became an admirer of Blake's work. Blake's first collection of poems, ''Poetical Sketches'', was published circa 1783. After his father's death, William and his brother Robert opened a print shop in 1784, and began working with radical publisher [[Joseph Johnson (publisher)|Joseph Johnson]]. Johnson's house was a place of meeting for some of the leading intellectual dissidents of the time in England: [[Joseph Priestley]], scientist; [[Richard Price]], philosopher; [[John Henry Fuseli]];<ref>[http://www.arthistoryarchive.com/arthistory/romanticism/Henry-Fuseli-William-Blake.html Biographies of William Blake and Henry Fuseli], retrieved on May 31st 2007.</ref> [[Mary Wollstonecraft]], an early feminist; and [[Thomas Paine]], American revolutionary. Along with [[William Wordsworth]] and [[William Godwin]], Blake had great hopes for the American and [[French revolution]] and wore a [[Phrygian cap]] in solidarity with the French revolutionaries, but despaired with the rise of [[Maximilien Robespierre|Robespierre]] and the [[Reign of Terror]] in the French revolution.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Blake illustrated ''[[Original Stories from Real Life]]'' (1788; 1791) by [[Mary Wollstonecraft]]. They seem to have shared some views on sexual equality and the institution of marriage, but there is no evidence proving without doubt that they actually met. In 1793's ''[[Visions of the Daughters of Albion]]'', Blake condemned the cruel absurdity of enforced chastity and marriage without love and defended the right of women to complete self-fulfillment.
| |
| − | ===Relief etching===
| |
| − | | |
| − | In 1788, at the age of 31, Blake began to experiment with [[Etching#Variants: Aquatint, soft-ground and relief etching|relief etching]], a method he would use to produce most of his books, paintings, pamphlets and of course his poems, including his longer 'prophecies' and his masterpiece the "Bible." The process is also referred to as illuminated printing, and final products as [[illuminated book]]s or prints. Illuminated printing involved writing the text of the poems on copper plates with pens and brushes, using an acid-resistant medium. Illustrations could appear alongside words in the manner of earlier [[illuminated manuscripts]]. He then etched the plates in acid in order to dissolve away the untreated copper and leave the design standing in relief (hence the name).
| |
| − | | |
| − | This is a reversal of the normal method of [[etching]], where the lines of the design are exposed to the acid, and the plate printed by the [[intaglio]] method. [[Relief etching]], which Blake invented, later became an important commercial printing method. The pages printed from these plates then had to be hand-coloured in water colours and stitched together to make up a volume. Blake used illuminated printing for most of his well-known works, including ''[[Songs of Innocence and Experience]]'', ''[[The Book of Thel]]'', ''[[The Marriage of Heaven and Hell]]'', and ''[[Jerusalem: The Emanation of The Giant Albion|Jerusalem]]''.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Later life and career==
| |
| − | Blake's marriage to Catherine remained a close and devoted one until his death. There were early problems such as Catherine's illiteracy and the couple's failure to produce children{{fact|date=April 2008}}. Gilchrist refers to "stormy times" in the early years of the marriage.<ref>Gilchrist, ''Life of William Blake'', 1863, p. 316</ref> Some biographers have suggested that Blake tried to bring a [[concubine]] into the marriage bed in accordance with the beliefs of the [[Emanuel Swedenborg|Swedenborgian Society]], <ref>Schuchard, MK, ''Why Mrs Blake Cried'', Century, 2006, p. 3</ref> but other scholars have dismissed these theories as conjecture. <ref>Ackroyd, Peter, ''Blake'', Sinclair-Stevenson, 1995, p. 82</ref> Blake taught Catherine to write, and she helped him to colour his printed poems.<ref>Bentley, G. E, ''Blake Records'', p 341</ref>
| |
| − | ===Felpham===
| |
| − | In 1800, Blake moved to a cottage at [[Felpham]] in Sussex (now [[West Sussex]]) to take up a job illustrating the works of [[William Hayley]], a minor poet. It was in this cottage that Blake wrote ''[[Milton: a Poem]]'' (published between 1805 and 1808). The preface to this work includes a poem beginning "And did those feet in ancient time", which became the words for the anthem, "[[And did those feet in ancient time|Jerusalem]]". Over time, Blake came to resent his new patron, coming to believe that Hayley was disinterested in true artistry, and preoccupied with "the meer drudgery of business".<ref name=milt>Blake, William. ''Milton a Poem, and the Final Illuminated Works''. 1998, page 14-5.</ref> Blake's disenchantment with Hayley has been speculated to have influenced ''[[Milton: a Poem]]'', in which Blake wrote that "Corporeal Friends are Spiritual Enemies" (3:26).<ref name=milt />
| |
| − | | |
| − | Blake's trouble with authority came to a head in August 1803, when he was involved in a physical altercation with a soldier called John Schofield.<ref>Wright, Thomas. ''Life of William Blake''. 2003, page 131.</ref> Blake was charged not only with assault, but also with uttering seditious and treasonable expressions against the King. Schofield claimed that Blake had exclaimed, "Damn the king. The soldiers are all slaves."<ref>[http://www.lilith-ezine.com/articles/williamblake1.html The Gothic Life of William Blake: 1757-1827]</ref> Blake would be cleared in the [[Chichester]] [[assize]]s of the charges. According to a report in the Sussex county paper, "The invented character of [the evidence] was ... so obvious that an acquittal resulted."<Ref>{{cite book |author=Lucas, E.V. |title=Highways and byways in Sussex |publisher=Macmillan |year=1904 |id=ASIN B-0008-5GBS-C}}</ref> Schofield was later depicted wearing "mind forged manacles" in an illustration to ''Jerusalem''.<ref>Peterfreund, Stuart,
| |
| − | ''The Din of the City in Blake's Prophetic Books'', ELH - Volume 64, Number 1, Spring 1997, pp. 99-130</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Return to London===
| |
| − | Blake returned to London in 1804 and began to write and illustrate ''[[Jerusalem: The Emanation of the Giant Albion|Jerusalem]]'' (1804–1820), his most ambitious work. Having conceived the idea of portraying the characters in [[Chaucer]]'s ''[[The Canterbury Tales|Canterbury Pilgrims]]'', Blake approached the dealer [[Robert Cromek]], with a view to marketing an engraving. Knowing that Blake was too eccentric to produce a popular work, Cromek promptly commissioned [[Thomas Stothard]] to execute the concept. When Blake learned that he had been cheated, he broke off contact with Stothard, formerly a friend. He also set up an independent exhibition in his brother's shop, designed to market his own version of the Chaucer illustration, along with other works. As a result he wrote his [[Descriptive Catalogue (1809)|''Descriptive Catalogue'']] (1809), which contains what [[Anthony Blunt]] has called a "brilliant analysis" of Chaucer. It is regularly anthologised as a classic of Chaucer criticism.<ref>Blunt, Anthony, ''The Art of William Blake'', p 77</ref> It also contained detailed explanations of his other paintings.
| |
| − | | |
| − | He was introduced by George Cumberland to a young artist named [[John Linnell (1792)|John Linnell]]. Through Linnell he met [[Samuel Palmer]], who belonged to a group of artists who called themselves the [[Ancients (art group)|Shoreham Ancients]]. This group shared Blake's rejection of modern trends and his belief in a spiritual and artistic New Age. At the age of 65 Blake began work on illustrations for the ''[[Book of Job]]''. These works were later admired by [[John Ruskin|Ruskin]], who compared Blake favourably to [[Rembrandt van Rijn|Rembrandt]], and by [[Ralph Vaughan Williams|Vaughan Williams]], who based his [[ballet]] ''[[Job, a masque for dancing|Job: A Masque for Dancing]]'' on a selection of the illustrations.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Later in his life Blake began to sell a great number of his works, particularly his [[Bible]] illustrations, to Thomas Butts, a patron who saw Blake more as a friend than a man whose work held artistic merit; this was typical of the opinions held of Blake throughout his life.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Dante's ''Inferno''====
| |
| − | The commission for [[Dante]]'s ''Inferno'' came to Blake in 1826 through [[John Linnell (painter)|Linnell]], with the ultimate aim of producing a series of engravings. Blake's death in 1827 would cut short the enterprise, and only a handful of the watercolours were completed, with only seven of the engravings arriving at proof form. Even so, they have evoked praise:
| |
| − | | |
| − | :'[T]he Dante [[watercolours]] are among Blake's richest achievements, engaging fully with the problem of illustrating a poem of this complexity. The mastery of watercolour has reached an even higher level than before, and is used to extraordinary effect in differentiating the atmosphere of the three states of being in the poem'.<ref>Bindman, David. "Blake as a Painter" in ''The Cambridge Guide to William Blake'', Morris Eaves (ed.), Cambridge, 2003, p. 106</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Blake's illustrations of the poem are not merely accompanying works, but rather seem to critically revise, or furnish commentary on, certain spiritual or moral aspects of the text. In illustrating ''[[Paradise Lost]]'', for instance, Blake seemed intent on revising Milton's focus on [[Satan]] as the central figure of the epic; for example, in ''Satan Watching the Endearments of Adam and Eve'' (1808), Satan occupies an isolated position at the picture's top, with [[Adam and Eve]] centered below. As if to emphasise the effects of the juxtaposition, Blake has shown Adam and Eve caught in an embrace, whereas Satan may only onanistically caress the serpent, whose identity he is close to assuming.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In this instance, because the project was never completed, Blake's intent may itself be obscured. Some indicators, however, bolster the impression that Blake's illustrations in their totality would themselves take issue with the text they accompany: In the margin of ''[[Homer]] Bearing the Sword and His Companions'', Blake notes, "Every thing in Dantes Comedia shews That for Tyrannical Purposes he has made This World the Foundation of All & the Goddess Nature & not the [[Holy Ghost]]." Blake seems to dissent from Dante's admiration of the poetic works of the [[ancient Greece|ancient Greeks]], and from the apparent glee with which Dante allots punishments in [[Hell]] (as evidenced by the grim humour of the [[canto]]s).
| |
| − | | |
| − | At the same time, Blake shared Dante's distrust of [[materialism]] and the corruptive nature of power, and clearly relished the opportunity to represent the atmosphere and imagery of Dante's work pictorially. Even as he seemed to near death, Blake's central preoccupation was his feverish work on the illustrations to [[Dante]]'s ''[[Divine Comedy|Inferno]]''; he is said to have spent one of the very last [[shilling]]s he possessed on a pencil to continue sketching.<ref>''Blake Records'', p. 341</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Death====
| |
| − | | |
| − | On the day of his death, Blake worked relentlessly on his Dante series. Eventually, it is reported, he ceased working and turned to his wife, who was in tears by his bedside. Beholding her, Blake is said to have cried, "Stay Kate! Keep just as you are – I will draw your portrait – for you have ever been an angel to me." Having completed this portrait (now lost), Blake laid down his tools and began to sing hymns and verses.<ref>Ackroyd, ''Blake'', 389</ref> At six that evening, after promising his wife that he would be with her always, Blake died. Gilchrist reports that a female lodger in the same house, present at his expiration, said, "I have been at the death, not of a man, but of a blessed angel."<ref>Gilchrist, ''The Life of William Blake'', London, 1863, 405</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Since 1965, the exact location of William Blake's grave had been lost and forgotten, while gravestones were taken away to create a new lawn. Nowadays, William Blake’s grave is commemorated by a stone that reads 'nearby lie the remains of William Blake and his wife Catherine Sophia'. This memorial stone is situated approximately 20 metres away from William Blake’s grave. The actual spot of Blake’s grave is not marked.
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[George Richmond]] gives the following account of Blake's death in a letter to [[Samuel Palmer]]:
| |
| − | {{cquote|He died ... in a most glorious manner. He said He was going to that Country he had all His life wished to see & expressed Himself Happy, hoping for [[Salvation]] through [[Jesus Christ]] — Just before he died His Countenance became fair. His eyes Brighten'd and he burst out Singing of the things he saw in Heaven.<ref>Grigson, ''Samuel Palmer'', p. 38</ref>}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | Catherine paid for Blake's funeral with money lent to her by Linnell. He was buried five days after his death – on the eve of his forty-fifth wedding anniversary – at the Dissenter's burial ground in [[Bunhill Fields]], where his parents were also interred. Present at the ceremonies were Catherine, [[Edward Calvert (painter)|Edward Calvert]], George Richmond, [[Frederick Tatham]] and John Linnell. Following Blake's death, Catherine moved into Tatham's house as a housekeeper. During this period, she believed she was regularly visited by Blake's spirit. She continued selling his illuminated works and paintings, but would entertain no business transaction without first "consulting Mr. Blake".<ref>Ackroyd, ''Blake'', 390</ref> On the day of her own death, in October 1831, she was as calm and cheerful as her husband, and called out to him "as if he were only in the next room, to say she was coming to him, and it would not be long now".<ref>''Blake Records'', p. 410</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | On her death, Blake's manuscripts were inherited by [[Frederick Tatham]], who burned several of those which he deemed heretical or too politically radical. Tatham had become an [[Edward Irving|Irvingite]], one of the many fundamentalist movements of the 19th century, and was severely opposed to any work that smacked of [[blasphemy]].<ref>Ackroyd, ''Blake'', p. 391</ref> Sexual imagery in a number of Blake's drawings was also erased by John Linnell.<ref>Marsha Keith Schuchard, ''Why Mrs Blake Cried: Swedenborg, Blake and the Sexual Basis of Spiritual Vision'', pp. 1-20</ref> Blake is now recognised as a [[saint]] in the [[Ecclesia Gnostica Catholica]]. The [[Blake Prize for Religious Art]] was established in his honour in [[Australia]] in 1949. In 1957 a memorial was erected in Westminster Abbey, in memory of him and his wife.<ref>{{cite web | author= Tate UK | year= | title= William Blake's London | url=http://www.tate.org.uk/learning/learnonline/blakeinteractive/lambeth/london_05.html |accessdate=2006-08-26}}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Religious views==
| |
| − | Although Blake's attacks on conventional [[religion]] were shocking in his own day, his rejection of religiosity was not a rejection of religion ''per se''. His view of orthodoxy is evident in ''The Marriage of Heaven and Hell'', a series of texts written in imitation of [[Biblical prophecy]]. Therein, Blake lists several ''Proverbs of Hell'', amongst which are the following:
| |
| − | | |
| − | ::Prisons are built with stones of Law, Brothels with bricks of Religion.
| |
| − | ::As the caterpillar chooses the fairest leaves to lay her eggs on, so the priest lays his curse on the fairest joys.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In ''The Everlasting Gospel'', Blake does not present [[Jesus]] as a [[philosopher]] or traditional messianic figure but as a supremely creative being, above dogma, logic and even morality:
| |
| − | ::If he had been Antichrist, Creeping Jesus,
| |
| − | ::He'd have done anything to please us:
| |
| − | ::Gone sneaking into the Synagogues
| |
| − | ::And not used the Elders & Priests like Dogs,
| |
| − | ::But humble as a Lamb or an Ass,
| |
| − | ::Obey himself to [[Caiaphas]].
| |
| − | ::God wants not man to humble himself
| |
| − | | |
| − | Jesus, for Blake, symbolises the vital relationship and unity between divinity and humanity: "[A]ll had originally one language and one religion: this was the religion of Jesus, the everlasting Gospel. Antiquity preaches the Gospel of Jesus." <ref name ="Raine">{{cite book | last = Raine | first = Kathleen | title = William Blake | publisher = Oxford University Press | date = 1970 | pages = 14-15| isbn = 0500201072}}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Blake designed his own mythology, which appears largely in his prophetic books. Within these Blake describes a number of characters, including 'Urizen', 'Enitharmon', 'Bromion' and 'Luvah'. This mythology seems to have a basis in the Bible and in [[Greek mythology]],<ref>"a personal mythology parallel to the Old Testament and Greek mythology"; Bonnefoy, Yves. ''Roman and European Mythologies''. 1992, page 265.</ref> and it accompanies his ideas about the everlasting Gospel.
| |
| − | | |
| − | {| class="toccolours" style="float: right; margin-left: 1em; margin-right: 1em; font-size: 85%; background:#eeeeee; color:black; width:23em; max-width: 25%;" cellspacing="5"
| |
| − | | style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | "I must Create a System, or be enslav'd by another Man's.
| |
| − | I will not Reason & Compare; my business is to Create."
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: left;" | Words uttered by Los in Blake's ''[[Jerusalem: The Emanation of the Giant Albion]]''.
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| − | One of Blake's strongest objections to [[orthodox Christianity]] is that he felt it encouraged the suppression of natural desires and discouraged earthly joy. In ''A Vision of the Last Judgement'', Blake says that:
| |
| − | {{cquote|Men are admitted into Heaven not because they have curbed & govern'd their Passions or have No Passions, but because they have Cultivated their Understandings. The Treasures of Heaven are not Negations of Passion, but Realities of Intellect, from which all the Passions Emanate Uncurbed in their Eternal Glory.}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | One may also note his words concerning religion in ''[[The Marriage of Heaven and Hell]]'':
| |
| − | {{cquote|All Bibles or sacred codes have been the causes of the following Errors.
| |
| − | | |
| − | :1. That Man has two real existing principles Viz: a Body & a Soul.
| |
| − | :2. That Energy, call'd Evil, is alone from the Body, & that Reason, call'd Good, is alone from the Soul.
| |
| − | :3. That God will torment Man in Eternity for following his Energies.
| |
| − | | |
| − | But the following Contraries to these are True
| |
| − | | |
| − | :1. Man has no Body distinct from his Soul for that call'd Body is a portion of Soul discern'd by the five Senses, the chief inlets of Soul in this age.
| |
| − | :2. Energy is the only life and is from the Body and Reason is the bound or outward circumference of Energy.
| |
| − | :3. Energy is Eternal Delight.}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | Blake does not subscribe to the notion of a distinct [[body]] from the [[soul]], and which must submit to the rule of soul, but rather sees body as an extension of soul derived from the 'discernment' of the senses. Thus, the emphasis orthodoxy places upon the denial of bodily urges is a dualistic error born of misapprehension of the relationship between body and soul; elsewhere, he describes Satan as the 'State of Error', and as being beyond salvation.<ref>{{cite book |last=Damon |first=Samuel Foster |authorlink= |coauthors= |title=A Blake Dictionary (Revised Edition) |year=1988 |publisher=Brown University Press |location= |pages=358 |isbn=0874514363 }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Blake opposed the [[sophistry]] of [[theology|theological]] thought that excuses [[pain]], admits [[evil]] and apologises for [[injustice]]. He abhorred self-denial,<ref>Makdisi, Saree. ''William Blake and the Impossible History of the 1790s''. 2003, page 226-7.</ref> which he associated with religious repression and particularly with sexual repression:<ref>Altizer, Thomas J.J. ''The New Apocalypse: The Radical Christian Vision of William Blake''. 2000, page 18.</ref> "Prudence is a rich ugly old maid courted by Incapacity. / He who desires but acts not, breeds pestilence."<ref>Blake, William. ''Proverbs of Hell'', via ''The Complete Poetry and Prose of William Blake''. 1982, page 35.</ref> He saw the concept of '[[sin]]' as a trap to bind men’s desires (the briars of ''Garden of Love''), and believed that restraint in obedience to a moral code imposed from the outside was against the spirit of life:
| |
| − | :Abstinence sows sand all over
| |
| − | :The ruddy limbs & flaming hair,
| |
| − | :But Desire Gratified
| |
| − | :Plants fruits & beauty there.
| |
| − | | |
| − | He did not hold with the [[doctrine]] of God as Lord, an entity separate from and superior to mankind<ref>{{cite book |last=Blake|first=Gerald Eades Bentley |authorlink= |coauthors= |title=William Blake: The Critical Heritage |year=1975 |publisher=Routledge & K. Paul |location=London |pages=30 |isbn=0710082347}}</ref>; this is shown clearly in his words about Jesus Christ: "He is the only God ... and so am I, and so are you." A telling phrase in ''The Marriage of Heaven and Hell'' is "men forgot that All deities reside in the human breast". This is very much in line with his belief in [[liberty]] and [[equality]] in society and between the sexes.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Assessment==
| |
| − | ===Creative mindset===
| |
| − | [[Northrop Frye]], commenting on Blake's consistency in strongly held views, notes that Blake "himself says that his notes on [Joshua] Reynolds, written at fifty, are 'exactly Similar' to those on Locke and Bacon, written when he was 'very Young'. Even phrases and lines of verse will reappear as much as forty years later. Consistency in maintaining what he believed to be true was itself one of his leading principles ... Consistency, then, foolish or otherwise, is one of Blake's chief preoccupations, just as 'self-contradiction' is always one of his most contemptuous comments".<ref name="fearfulsymmetry">[[Northrop Frye]], ''Fearful Symmetry: A Study of William Blake'', 1947, [[Princeton University Press]]</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Blake abhorred [[slavery]] and believed in racial and sexual equality.<ref>[http://www.feministezine.com/feminist/williamblake2.html William Blake's Ecofeminism], retrieved on May 31st 2007.</ref> Several of his poems and paintings express a notion of universal humanity: "As all men are alike (tho' infinitely various)". In one poem, narrated by a black child, white and black bodies alike are described as shaded groves or clouds, which exist only until one learns "to bear the beams of love":
| |
| − | | |
| − | :When I from black, and he from white cloud free,
| |
| − | :And round the tent of God like lambs we joy,
| |
| − | | |
| − | :I'll shade him from the heat till he can bear
| |
| − | :To lean in joy upon our Father's knee;
| |
| − | :And then I'll stand and stroke his silver hair,
| |
| − | :And be like him, and he will then love me.
| |
| − | | |
| − | (Blake, William and Rossetti, William Michael. ''[http://books.google.com/books?id=fGYLAAAAIAAJ&pg=PP11&dq=%22The+Poetical+Works+of+William+Blake:+Lyrical+and+Miscellaneous%22&lr=&as_brr=3 The Poetical Works of William Blake: Lyrical and Miscellaneous]''. 1890, page 81-2.)
| |
| − | | |
| − | Blake retained an active interest in social and political events for all his life, often cloaking social and political statements in mystical [[allegory]]. His views on what he saw as oppression and restriction of rightful freedom extended to the Church. His spiritual beliefs are evidenced in ''Songs of Experience'' (1794), in which he distinguishes between the [[Old Testament]] [[God]], whose restrictions he rejected, and the [[New Testament]] God ([[Jesus Christ]] in [[Trinitarianism]]), whom he saw as a positive influence.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Visions===
| |
| − | From a young age, William Blake claimed to have seen [[Vision (religion)|visions]]. The earliest of these visions may have occurred as early as the age of four when, according to one anecdote, the young artist "saw God" when God "put his head to the window", causing Blake to break into screaming.<ref name=bent78>Bentley, Gerald Eades and Bentley Jr., G. ''William Blake: The Critical Heritage''. 1995, page 36-7.</ref> At the age of eight or ten in [[Peckham Rye]], [[London]], Blake claimed to have seen "a tree filled with angels, bright angelic wings bespangling every bough like stars."<ref name=bent78 /> According to Blake's [[Victorian era|Victorian]] biographer Gilchrist, he returned home and reported this vision, and he only escaped being thrashed by his father for telling a lie through the intervention of his mother. Though all evidence suggests that his parents were largely supportive, his mother seems to have been especially so, and several of Blake's early drawings and poems decorated the walls of her chamber. On another occasion, Blake watched haymakers at work, and thought he saw angelic figures walking among them.<ref name=bent78 />
| |
| − | | |
| − | Blake claimed to experience visions throughout his life. They were often associated with beautiful religious themes and imagery, and therefore may have inspired him further with spiritual works and pursuits. Certainly, religious concepts and imagery figure centrally in Blake's works. [[God]] and [[Christianity]] constituted the intellectual centre of his writings, from which he drew inspiration. In addition, Blake believed that he was personally instructed and encouraged by [[Archangel]]s to create his artistic works, which he claimed were actively read and enjoyed by those same Archangels. In a letter to [[William Hayley]], dated May 6, 1800, Blake writes:
| |
| − | <blockquote>I know that our deceased friends are more really with us than when they were apparent to our mortal part. Thirteen years ago I lost a brother, and with his spirit I converse daily and hourly in the spirit, and see him in my remembrance, in the region of my imagination. I hear his advice, and even now write from his dictate.</blockquote>
| |
| − | | |
| − | In a letter to [[John Flaxman]], dated September 21, 1800, Blake writes:
| |
| − | <blockquote>[The town of] Felpham is a sweet place for Study, because it is more spiritual than London. Heaven opens here on all sides her golden Gates; her windows are not obstructed by vapours; voices of Celestial inhabitants are more distinctly heard, & their forms more distinctly seen; & my Cottage is also a Shadow of their houses. My Wife & Sister are both well, courting Neptune for an embrace... I am more famed in Heaven for my works than I could well conceive. In my Brain are studies & Chambers filled with books & pictures of old, which I wrote & painted in ages of Eternity before my mortal life; & those works are the delight & Study of Archangels.</blockquote>
| |
| − | | |
| − | In a letter to Thomas Butts, dated April 25, 1803, Blake writes:
| |
| − | <blockquote>Now I may say to you, what perhaps I should not dare to say to anyone else: That I can alone carry on my visionary studies in London unannoy'd, & that I may converse with my friends in Eternity, See Visions, Dream Dreams & prophecy & speak Parables unobserv'd & at liberty from the Doubts of other Mortals; perhaps Doubts proceeding from Kindness, but Doubts are always pernicious, Especially when we Doubt our Friends.</blockquote>
| |
| − | | |
| − | In ''A Vision of the Last Judgement'' Blake writes:
| |
| − | <blockquote>Error is Created. Truth is Eternal. Error, or Creation, will be Burned up, & then, & not till Then, Truth or Eternity will appear. It is Burnt up the Moment Men cease to behold it. I assert for My Self that I do not behold the outward Creation & that to me it is hindrance & not Action; it is as the Dirt upon my feet, No part of Me. "What," it will be Question'd, "When the Sun rises, do you not see a round disk of fire somewhat like a Guinea?" Oh no, no, I see an Innumerable company of the Heavenly host crying, 'Holy, Holy, Holy, is the Lord God Almighty.' I question not my Corporeal or Vegetative Eye any more than I would Question a Window concerning Sight. I look thro' it & not with it.<ref>Blake, William. ''Complete Writings with Variant Readings''. 1969, page 617.</ref></blockquote>
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[William Wordsworth]] remarked, "There was no doubt that this poor man was mad, but there is something in the madness of this man which interests me more than the sanity of [[Lord Byron]] and [[Walter Scott]]."<ref>{{cite web | title = Blake's vision on show | author = John Ezard | url = http://arts.guardian.co.uk/news/story/0,,1254856,00.html#article_continue | publisher = [[The Guardian]] | date = 2004-07-06 | accessdate = 2008-03-24}}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | D.C.Williams (1899-1983) said that Blake was a romantic with a critical view on the world, he maintained that Blake's ''[[Songs of Innocence and Experience|Songs of Innocence]]'' were made as a view of an ideal, somewhat [[Utopian]] view whereas he used the ''[[Songs of Innocence and Experience|Songs of Experience]]'' in order to show the suffering and loss posed by the nature of society and the world of his time.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==In popular culture==
| |
| − | In addition to his influence on writers and artists, Blake's role as a song-writer and as an exponent of sexual and imaginative freedom have made him an influential figure in popular culture, especially since the 1960s. Far more than any other canonical writer, his work has influenced and been adapted by popular musicians including [[Billy Bragg]], [[Emerson, Lake & Palmer]], [[Mike Westbrook]], [[U2]], [[Van Morrison]], [[Nick Drake]],<ref> Macdonald, Ian, [http://www.algonet.se/~iguana/DRAKE/exiled1.html "Nick Drake: Exiled From Heaven 1"], Retrieved on [[2008-06-27]].</ref> [[Jah Wobble]], [[Tangerine Dream]], [[Bruce Dickinson]], [[David Axelrod]], [[Mark E. Smith]], [[Kathleen Yearwood]] and [[Ulver]]. Folk musicians have also adapted his work, and figures such as [[Bob Dylan]] and [[Allen Ginsberg]] have been influenced by him. The genre of the [[graphic novel]] traces its origins to Blake's etched songs and Prophetic Books.<ref>[http://www.skinnymag.co.uk/content/view/5794/ Jay Shukla, ''William Blake - The Divine Image'']</ref> Abstract painter [[Ronnie Landfield]] dedicated a painting to Blake [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lyrical_Abstraction#Lyrical_Abstraction_in_America] in the late 1960s. Children's author [[Maurice Sendak]] and exponents such as [[Grant Morrison]], [[Robert Crumb]], and [[J.M. DeMatteis]] have all cited Blake as one of their major inspirations.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Bibliography==
| |
| − | ===Illuminated books===
| |
| − | *c.1788: ''[[All Religions Are One]]''
| |
| − | **''[[There Is No Natural Religion]]''
| |
| − | *1789: ''[[Songs of Innocence]]''
| |
| − | ** ''[[The Book of Thel]]''
| |
| − | *1790–1793: ''[[The Marriage of Heaven and Hell]]''
| |
| − | *1793: ''[[Visions of the Daughters of Albion]]''
| |
| − | ** ''[http://www.english.uga.edu/nhilton/Blake/blaketxt1/america_a_prophecy.html America: a Prophecy]''
| |
| − | *1794: ''[[Europe: a Prophecy]]''
| |
| − | **''[[The First Book of Urizen]]''
| |
| − | ** ''[[Songs of Experience]]''
| |
| − | *1795: ''[[The Book of Los]]''
| |
| − | ** ''[[The Song of Los]]''
| |
| − | ** ''[[The Book of Ahania]]''
| |
| − | *c.1804–c.1811: ''[[Milton: a Poem]]''
| |
| − | *1804–1820: ''[[Jerusalem: The Emanation of The Giant Albion]]''
| |
| − | ===Non-Illuminated===
| |
| − | *1783: ''[[Wikisource:Poetical Sketches|Poetical Sketches]]''
| |
| − | *1789: ''[[Tiriel (Blake)|Tiriel]]''
| |
| − | *1791: ''[[The French Revolution (Blake)|The French Revolution]]''
| |
| − | *1797: ''[[The Four Zoas (Blake)|The Four Zoas]]''
| |
| − | ===Illustrated by Blake===
| |
| − | *1791: [[Mary Wollstonecraft]], ''[[Original Stories from Real Life]]''
| |
| − | *1797: [[Edward Young]], ''[[Night Thoughts (poem)|Night Thoughts]]''
| |
| − | *1805-1808: [[Robert Blair (poet)|Robert Blair]], ''The Grave''
| |
| − | *1808: [[John Milton]], ''[[Paradise Lost]]''
| |
| − | *1819-1820: [[John Varley (painter)|John Varley]], ''Visionary Heads''
| |
| − | *1821: [[R.J. Thornton]], ''Virgil''
| |
| − | *1823-1826: ''[[Book of Job|The Book of Job]]''
| |
| − | *1825-1827: [[Dante Alighieri|Dante]], ''[[The Divine Comedy]]'' (Blake died in 1827 with these watercolours still unfinished)
| |
| − | ===On Blake===
| |
| − | *[[Peter Ackroyd]] (1995). ''Blake''. Sinclair-Stevenson. ISBN 1-85619-278-4.
| |
| − | *[[Donald Ault]] (1974). ''Visionary Physics: Blake's Response to Newton''. University of Chicago. ISBN 0-226-03225-6.
| |
| − | *(1987). ''Narrative Unbound: Re-Visioning William Blake's The Four Zoas''. Station Hill Press. ISBN-10 1886449759.
| |
| − | *[[G.E. Bentley Jr.]] (2001). ''The Stranger From Paradise: A Biography of William Blake''. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-08939-2.
| |
| − | *[[Harold Bloom]] (1963). ''Blake’s Apocalypse''. Doubleday.
| |
| − | *[[Jacob Bronowski]] (1972). ''William Blake and the Age of Revolution''. Routledge and K. Paul. ISBN 0-7100-7277-5 (hardcover) ISBN 0-7100-7278-3 (pbk.)
| |
| − | *(1967). ''William Blake, 1757-1827; a man without a mask''. Haskell House Publishers.
| |
| − | *[[G. K. Chesterton]] (1920s). ''William Blake''. House of Stratus ISBN 0-7551-0032-8.
| |
| − | *[[S. Foster Damon]] (1979). ''A Blake Dictionary''. Shambhala. ISBN 0-394-73688-5.
| |
| − | *[[David V. Erdman]] (1977). ''Blake: Prophet Against Empire: A Poet's Interpretation of the History of His Own Times''. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-486-26719-9.
| |
| − | *Irving Fiske (1951). "Bernard Shaw's Debt to William Blake." (Shaw Society)
| |
| − | *[[Northrop Frye]] (1947). ''Fearful Symmetry''. Princeton Univ Press. ISBN 0-691-06165-3.
| |
| − | *[[Alexander Gilchrist]], ''Life and Works of William Blake'', (second edition, London, 1880)
| |
| − | *[[James King (author)|James King]] (1991). ''William Blake: His Life''. St. Martin's Press. ISBN 0-312-07572-3.
| |
| − | *[[Benjamin Heath Malkin]] (1806). ''A Father's Memoirs of his Child''.
| |
| − | *[[Peter Marshall (author)|Peter Marshall]] (1988). ''William Blake: Visionary Anarchist'' ISBN 0-900384-77-8
| |
| − | *[[W.J.T. Mitchell]] (1978). ''Blake's Composite Art: A Study of the Illuminated Poetry''. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-691-01402-7.
| |
| − | *[[Victor N. Paananen]] (1996). ''William Blake''. Twayne Publishers. ISBN 0-8057-7053-4.
| |
| − | *[[George Anthony Rosso Jr.]] (1993). ''Blake's Prophetic Workshop: A Study of The Four Zoas''. Associated University Presses. ISBN 0-8387-5240-3.
| |
| − | *Sheila A. Spector (2001). ''"Wonders Divine": the development of Blake's Kabbalistic myth'', (Bucknell UP)
| |
| − | *[[Algernon Swinburne]], ''William Blake: A Critical Essay'', (London, 1868)
| |
| − | *[[E.P. Thompson]] (1993). ''Witness against the Beast''. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-22515-9.
| |
| − | *W. M. Rosetti (editor), ''Poetical Works of William Blake'', (London, 1874)
| |
| − | *A. G. B. Russell (1912). ''Engravings of William Blake''.
| |
| − | *[[Basil de Sélincourt]], ''William Blake'', (London, 1909)
| |
| − | *Joseph Viscomi (1993). ''Blake and the Idea of the Book'', (Princeton UP). ISBN 0-691-06962-X.
| |
| − | *David Weir (2003). ''Brahma in the West: William Blake and the Oriental Renaissance'', (SUNY Press)
| |
| − | *Jason Whittaker (1999). ''William Blake and the Myths of Britain'', (Macmillan)
| |
| − | *[[William Butler Yeats]] (1903). ''Ideas of Good and Evil''. Contains essays.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==References==
| |
| − | #Frye, Northrop and Denham, Robert D. Collected Works of Northrop Frye. 2006, page 11-2.
| |
| − | #Jones, Jonathan (2005-04-25). "Blake's heaven". The Guardian.
| |
| − | #Thomas, Edward. A Literary Pilgrim in England. 1917, page 3.
| |
| − | #Yeats, W. B. The Collected Works of W. B. Yeats. 2007, page 85.
| |
| − | #Wilson, Mona. The Life of William Blake. The Nonesuch Press, 1927. p.167.
| |
| − | #The New York Times Guide to Essential Knowledge. 2004, page 351.
| |
| − | #Blake, William. Blake's "America, a Prophecy" ; And, "Europe, a Prophecy". 1984, page 2.
| |
| − | #Kazin, Alfred (1997). "An Introduction to William Blake". Retrieved on 2006-09-23.
| |
| − | #Blake, William and Rossetti, William Michael. The Poetical Works of William Blake: Lyrical and Miscellaneous. 1890, page xi.
| |
| − | #Blake, William and Rossetti, William Michael. The Poetical Works of William Blake: Lyrical and Miscellaneous. 1890, page xiii.
| |
| − | #poets.org/William Blake, retrieved online June 13, 2008
| |
| − | #Bentley, Gerald Eades and Bentley Jr., G. William Blake: The Critical Heritage. 1995, page 34-5.
| |
| − | #Raine, Kathleen (1970). World of Art: William Blake. Thames & Hudson. ISBN 0-500-20107-2.
| |
| − | #Blake, Peter Ackroyd, Sinclair-Stevenson, 1995
| |
| − | #Blake, William. The Poems of William Blake. 1893, page xix.
| |
| − | #Blake, Ackroyd
| |
| − | #Blake, William and Tatham, Frederick. The Letters of William Blake: Together with a Life. 1906, page 7.
| |
| − | #Erdman, David V. The Complete Poetry and Prose of William Blake, 2nd edition, p641. ISBN 0-385-15213-2.
| |
| − | #Gilchrist, A, The Life of William Blake, London, 1842, p. 30
| |
| − | #Erdman, David, Prophet Against Empire, p. 9
| |
| − | #McGann, J. "Did Blake Betray the French Revolution", Presenting Poetry: Composition, Publication, Reception, Cambridge University Press, 1995, p.128
| |
| − | #Biographies of William Blake and Henry Fuseli, retrieved on May 31st 2007.
| |
| − | #Baker-Smith, Dominic. Between Dream and Nature: Essays on Utopia and Dystopia. 1987, page 163.
| |
| − | #Kaiser, Christopher B. Creational Theology and the History of Physical Science. 1997, page 328.
| |
| − | #Gilchrist, Life of William Blake, 1863, p. 316
| |
| − | #Ackroyd, Peter, Blake, Sinclair-Stevenson, 1995, p. 82
| |
| − | #Bentley, G. E, Blake Records, p 341
| |
| − | #Blake, William. Milton a Poem, and the Final Illuminated Works. 1998, page 14-5.
| |
| − | #Wright, Thomas. Life of William Blake. 2003, page 131.
| |
| − | #The Gothic Life of William Blake: 1757-1827
| |
| − | #Lucas, E.V. (1904). Highways and byways in Sussex. Macmillan. ASIN B-0008-5GBS-C.
| |
| − | #Peterfreund, Stuart, The Din of the City in Blake's Prophetic Books, ELH - Volume 64, Number 1, Spring 1997, pp. 99-130
| |
| − | #Blunt, Anthony, The Art of William Blake, p 77
| |
| − | #Bindman, David. "Blake as a Painter" in The Cambridge Guide to William Blake, Morris Eaves (ed.), Cambridge, 2003, p. 106
| |
| − | #Blake Records, p. 341
| |
| − | #Ackroyd, Blake, 389
| |
| − | #Gilchrist, The Life of William Blake, London, 1863, 405
| |
| − | #Grigson, Samuel Palmer, p. 38
| |
| − | #Ackroyd, Blake, 390
| |
| − | #Blake Records, p. 410
| |
| − | #Ackroyd, Blake, p. 391
| |
| − | #Marsha Keith Schuchard, Why Mrs Blake Cried: Swedenborg, Blake and the Sexual Basis of Spiritual Vision, pp. 1-20
| |
| − | #Tate UK. "William Blake's London". Retrieved on 2006-08-26.
| |
| − | # "a personal mythology parallel to the Old Testament and Greek mythology"; Bonnefoy, Yves. Roman and European Mythologies. 1992, page 265.
| |
| − | #Damon, Samuel Foster (1988). A Blake Dictionary (Revised Edition). Brown University Press, 358. ISBN 0874514363.
| |
| − | #Makdisi, Saree. William Blake and the Impossible History of the 1790s. 2003, page 226-7.
| |
| − | #Altizer, Thomas J.J. The New Apocalypse: The Radical Christian Vision of William Blake. 2000, page 18.
| |
| − | #Blake, William. Proverbs of Hell, via The Complete Poetry and Prose of William Blake. 1982, page 35.
| |
| − | #Blake, Gerald Eades Bentley (1975). William Blake: The Critical Heritage. London: Routledge & K. Paul, 30. ISBN 0710082347.
| |
| − | #Northrop Frye, Fearful Symmetry: A Study of William Blake, 1947, Princeton University Press
| |
| − | #William Blake's Ecofeminism, retrieved on May 31st 2007.
| |
| − | #Blake, William and Rossetti, William Michael. The Poetical Works of William Blake: Lyrical and Miscellaneous. 1890, page 81-2.
| |
| − | #Bentley, Gerald Eades and Bentley Jr., G. William Blake: The Critical Heritage. 1995, page 36-7.
| |
| − | #Langridge, Irene. William Blake: A Study of His Life and Art Work. 1904, page 48-9.
| |
| − | #Blake, William. Complete Writings with Variant Readings. 1969, page 617.
| |
| − | #John Ezard (2004-07-06). "Blake's vision on show". The Guardian. Retrieved on 2008-03-24.
| |
| − | #Macdonald, Ian, "Nick Drake: Exiled From Heaven 1", Retrieved on 2008-06-27.
| |
| − | #Jay Shukla, William Blake - The Divine Image
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==External links==
| |
| − | *[http://www.blakearchive.org/ The William Blake Archive], a hypermedia archive sponsored by the Library of Congress and supported by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
| |
| − | * [http://www.tate.org.uk/learning/learnonline/blakeinteractive/ Tate's online resource on William Blake with notes for teachers]
| |
| − | * [http://www.friendsofblake.org/ The recent re-discovery of the location of William Blake's grave]
| |
| − | * [http://www.bl.uk/onlinegallery/ttp/ttpbooks.html See Blake's notebook online using the British Library's Turning the Pages system (requires Shockwave).]
| |
| − | *[http://www.english.uga.edu/nhilton/Blake/blaketxt1/ Contents, The Complete Poetry and Prose of William Blake edited by David V. Erdman]
| |
| − | *[http://www.ngv.vic.gov.au/blake/ An Archive of an Exhibit of his Work at the National Gallery of Victoria]
| |
| − | *[http://www.the3graces.info/random_blake.htm Introduction to The Drawings and Engravings of William Blake, by Laurence Binyon]
| |
| − | *[http://www.sanjeev.net/poetry/blake-william/index.html Poetry Archive: 170 poems of William Blake]
| |
| − | *[http://ccbs.ntu.edu.tw/FULLTEXT/JR-JOCP/ferrar1.htm Ch'an Buddhism and the Prophetic Poems of William Blake]
| |
| − | *[http://www.johnwindle.com/book.jsp?id=10 A Blake Collector's Vade-Mecum]
| |
| − | *[http://www.english.ufl.edu/imagetext/archives/v3_2 William Blake and Visual Culture: A special issue of the journal ''ImageText'']
| |
| − | *[http://research.hrc.utexas.edu:8080/hrcxtf/view?docId=ead/00185.xml&query=blake,%20william&query-join=and William Blake Collection] at the [[Harry Ransom Center]] at the [[University of Texas at Austin]]
| |
| − | *[[Joseph Nechvatal]] [http://www.eyewithwings.net/nechvatal/Blake/BlakeVisionWWW.htm William Blake and Visionary Art]
| |
| − | *[http://www.kerouacalley.com/blake.html William Blake Multimedia Directory - <i>Kerouac Alley</i>]
| |
| | | | |
| | + | John Middleton Murry notes discontinuity between ''Marriage'' and the late works, in that while the early Blake focused on a "sheer negative opposition between [[Energy]] and [[Reason]]", the later Blake emphasised the notions of self-sacrifice and forgiveness as the road to interior wholeness. This [[renunciation]] of the sharper [[dualism]] of ''Marriage of Heaven and Hell'' is evidenced in particular by the humanisation of the character of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Urizen Urizen] in the later works. Middleton characterises the later Blake as having found "mutual understanding" and "mutual forgiveness". |
| | + | ==See also== |
| | + | *'''''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_blake#Bibliography Blake Bibliography]''''' |
| | [[Category:The Arts]] | | [[Category:The Arts]] |
| | [[Category: Languages and Literature]] | | [[Category: Languages and Literature]] |